
“A superior surgical method going beyond just ‘ablate’ the benign or malignant tumors.”
Macadam™ Ultrasonic Surgical Cavitation System
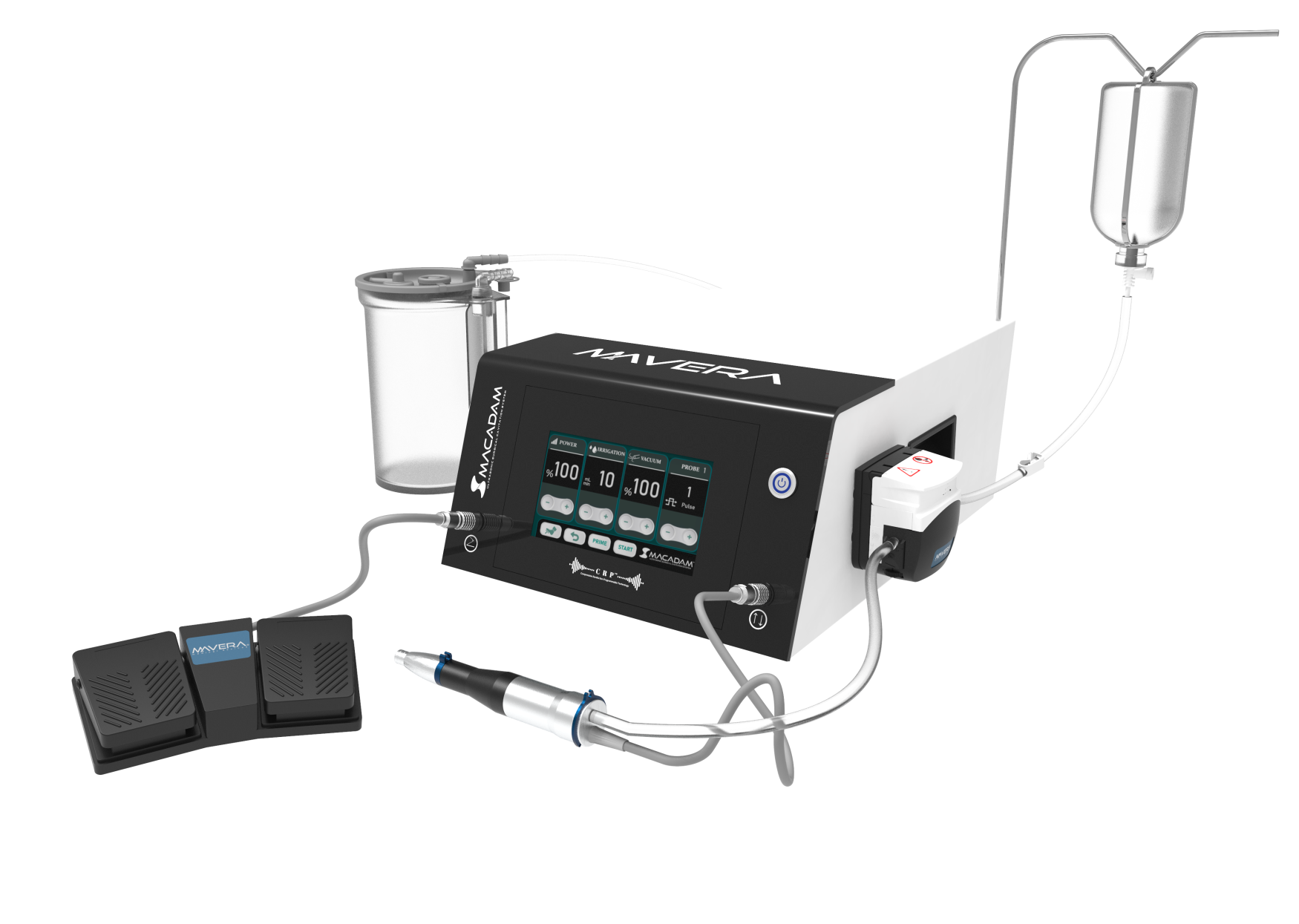 A
RevolutionaryDevice Offering Better Results in Ultrasonic Aspirator
A
RevolutionaryDevice Offering Better Results in Ultrasonic Aspirator
- Selectively killing cancer cells
- Less bleeding
- Versatile
Mechanism of Action
Macadam™ Ultrasonic Surgical Cavitation System is indicated for use in surgical procedures where fragmentation, emulsification resection and aspiration of soft and hard tissues are required in the following surgeries: including Neurosurgery, Gastrointestinal and affiliated organ surgery, Urological surgery, General Surgery, including removal of benign or malignant tumors or other unwanted tissue. When the vibrated probe interacts with biological tissue, the cells are fragmented as a result of both the ultrasonic pressure waves generated by the impact and by the resulting acoustic cavitation. Cavitation is the formation, growth, and implosion of vapor bubbles in the cellular liquid and is caused by the sound waves passing through the tissue. When these microbubbles implode, they generate a high-energy pressure wave that further fragments the tissue, enhancing the cellular disruption caused by the acoustic and mechanical forces generated by the vibrating tip.
Principle of Operation
Ultrasonic surgery is realized between 20-60 kHz. In principle, the outlet voltage is supplied at 50 to 60 hertz. The generator boosts the frequency to 25-36 K hertz. The resulting ultrasonic frequency is delivered into the hand-piece and amplified to the motion. After activation, the probe can vibrate 25.000-36.000 strokes per second and results in cavitation. The low frequency ultrasonic energy has ability to disintegrate several types of benign or malignant tumors without any harming healthy cells.
1) Selectively killing cancer cells
Macadam™ Ultrasonic Surgical Cavitation System selectively removes tissue based on their physical properties such as size, cell-wall thickness and size of the organelles within them while controlling the close bile ducts, arteries and vessels to the removing tissue. The studies indicated that differences between tissue strength of benign or malignant tumors and healthy cells can affect how they responses to ultrasonic frequency and how the oscillations trigger cell death. At the tip of the probe, controlled pulsed energy and reserve power creates a rebound effect while the tip reaches a structure that has rich collagen composition. Due to the tactile feedback mechanism surgeons could differentiate targeted benign or malignant tumors and other structures and control the probe before harming healthy tissue.
1
2) Less bleeding
Macadam™ Ultrasonic Surgical Cavitation System has also contributed to reduction in blood loss during surgical operation. It is indicated in a liver transection clinical study that these include better delineation of the transection plane with the use of intraoperative ultrasound, and better inflow and outflow control. Inflow occlusion and low central venous pressure anesthesia have been widely used to reduce bleeding from inflow vessels and hepatic veins in the transection surface. This article reviews the current techniques of liver transection and evidence from the literature on the efficacy of different techniques.
2
3) Versatile
Macadam™ Ultrasonic Surgical Cavitation System offers a wide range of choices o f tips for different procedures;
- The high amplitude of the 26 kHz frequency handpiece provides in a compact design engineered for ablation of soft tissues and deeper tissue penetration for advanced resection speed.
- The 36kHz frequency handpiece which combines high performance with flexibility is designed for tough and fibrous tissue removal. The reduced amplitude of the 36 kHz frequency handpiece delivers a more concentrated and controlled effect while the risk of collateral consequence is minimized.
Indications
Macadam™ Ultrasonic Surgical Cavitation System is indicated for use in surgical procedures where fragmentation, emulsification resection and aspiration of soft and hard tissues are required in the following surgeries: including Neurosurgery, Gastrointestinal and affiliated organ surgery, Urological surgery, Plastic and Reconstructive surgery, General surgery, Orthopedic surgery, Gynecological surgery, Thoracic surgery, Laparoscopic surgery and Thoracoscopic surgery. Gastrointestinal and Affiliated Organ Surgery - including removal of benign or malignant tumors or other unwanted tissue, including hepatic parenchyma, in open or laparoscopic procedures, hepatic resection, tumor resection, lobectomy or trisegmentectomy, or removal of tissue during liver allotransplantation and donor hepatectomy. Urological surgery - including removal of renal parenchyma during nephrectomy or partial nephrectomy. General Surgery - including removal of benign or malignant tumors or other unwanted soft tissue in open or minimally invasive general surgical procedures. Plastic and Reconstructive surgery- LipoSculpture (subcutaneous fatty tissue for aesthetic body contouring). Laparoscopic Surgery - including removal of hepatic parenchyma in laparoscopic hepatic resection, lobectomy or trisegmentectomy, in laparoscopic donor hepatectomy or laparoscopic cholecystectomy or laparoscopic pancreatic jejunostomy, or pancreatectomy, or laparoscopic appendectomy, laparoscopic colon resection or laparoscopic partial gastrectomy.




 A
A